IDEXX SDMA Resource Centre
Interpreting test results and next steps.

Interpreting your SDMA results
15–19 µg/dL
Take action when SDMA results are "high" (15 µg/dL and above). Follow the algorithm to determine if kidney disease is probable.
≥ 20 µg/dL
When SDMA result is ≥ 20 µg/dL, perform a complete urinalysis. Kidney disease is probable. Act immediately by following the protocol.
Use the protocol
IDEXX SDMA algorithm
An elevated SDMA* concentration is a reflection of impaired glomerular filtration rate (GFR). Both primary kidney disease and secondary kidney insults, such as concurrent disease, can cause an elevation in SDMA concentration. Follow this algorithm to investigate elevated SDMA concentrations and determine whether acute, active, or chronic injury is occurring. Also use the algorithm to follow up an increased SDMA with further investigation, management, and monitoring with the protocol.
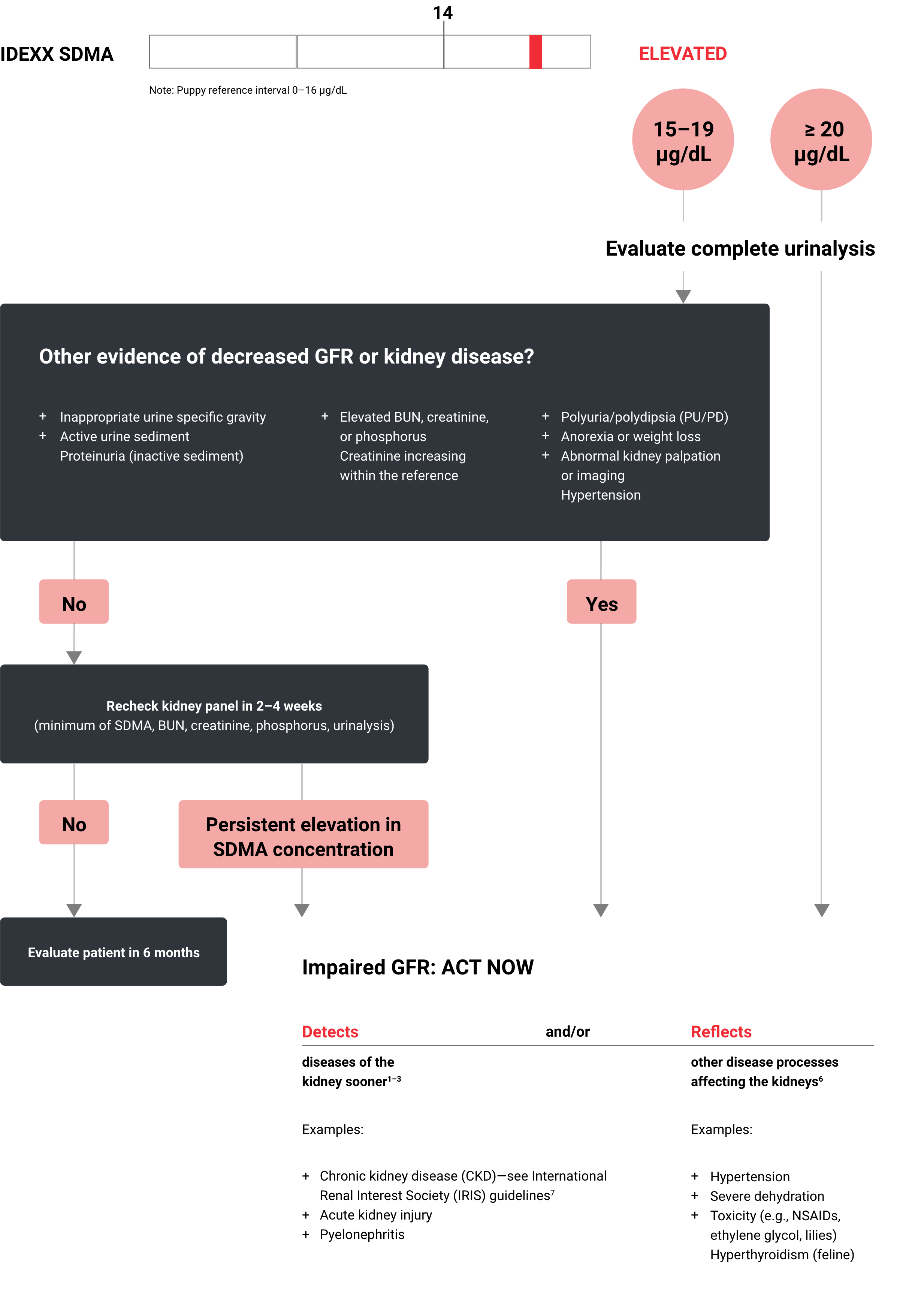
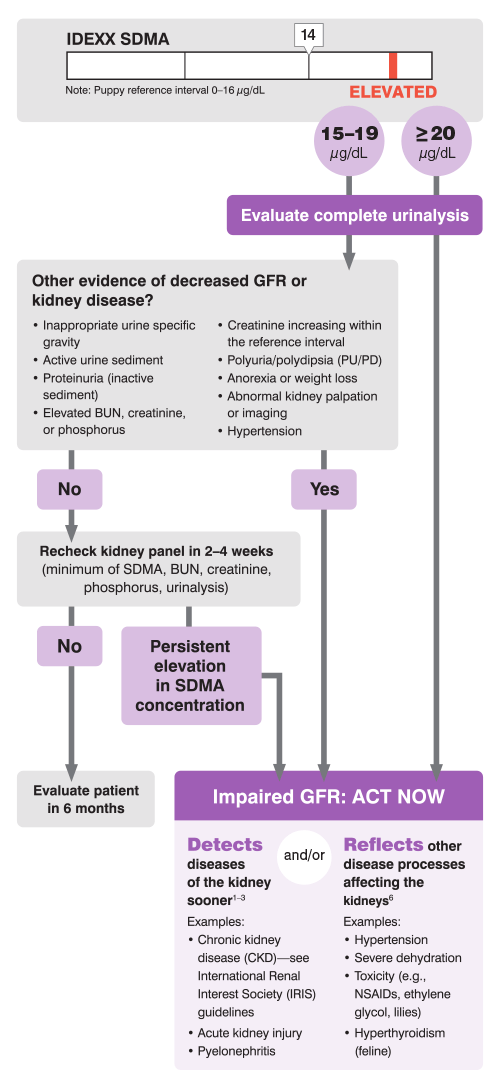
Initial steps in investigating, managing, and monitoring impaired GFR as identified by an elevated SDMA
Investigate
Underlying cause, treatable condition, concurrent disease, chronic kidney disease (CKD)
Underlying cause
- Urinary tract infection (UTI)/pyelonephritis
- Toxicity (e.g., NSAIDs, ethylene glycol, lilies)
- Acute kidney Injury
- Systemic hypertension
- Chronic kidney disease (CKD)
Consider performing
- Urine culture and minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) susceptibility
- Infectious disease testing
- Abdominal imaging
- Urine protein:creatine (UPC) ratio (proteinuria)
- Blood pressure
Concurrent condition to assess
- Hydration status
- Thyroid status (feline)
Manage
Treat underlying disease, manage assessed kidney injury, adjust care protocols
Treat appropriately
- Underlying disease (e.g., pyelonephritis, infectious disease)
- Dehydration
- Discontinue nephrotoxic medications (e.g., NSAIDs)
- Hypertension
- Proteinuria
Additional support
- Ample, clean water
- Kidney-supportive diet if warranted
Adjust anesthesia protocols
- Provide fluids (intravenous or subcutaneous)
- Oxygen support prior to, during, and after procedure
- Adjust pain management
Monitor
Manage and monitor outcomes
Monitor renal biomarkers
Trended testing of the following:
- SDMA, urea, creatinine, and phosphorus
- Urinalysis
- Blood pressure
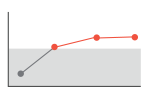
GFR impairment, stable
SDMA remains increased, but stable
- GFR remains impaired but stable
- Consider CKD diagnosis, refer to IRIS staging and treatment guidelines
- Institute appropriate supportive care and monitoring
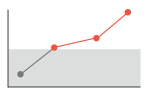
GFR impairment, progressive
SDMA continues to increase
- Ongoing active kidney injury
- Revisit investigate: repeat or additional diagnostics
- Institute ongoing supportive care
GFR restoration
SDMA returns to normal
- Recovery from mild injury
- Response to appropriate therapy
- Compensatory mechanisms
- Recheck within 6 months–1 year
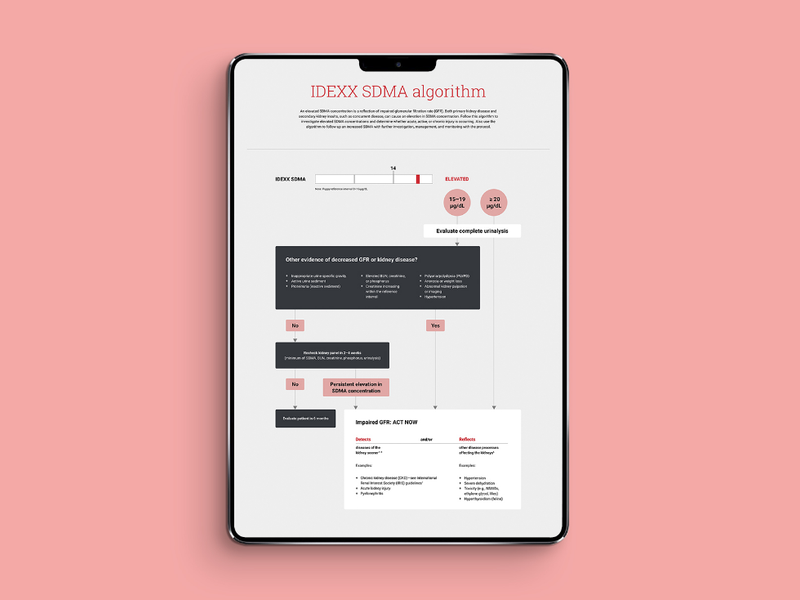
Get printable versions of the algorithm and protocol
Use the IDEXX SDMA algorithm to interpret results

When SDMA is increased and other markers are normal
Follow the IRIS guidelines to stage and treat chronic kidney disease
What is considered a normal SDMA range?
Any increase in SDMA concentration above the reference interval (greater than 14 µg/dL in cats and adult dogs; greater than 16µg/dL in puppies) is considered meaningful.
An elevated SDMA concentration is a reflection of impaired glomerular filtration rate (GFR). Both primary kidney disease
and secondary kidney insults, such as concurrent disease, can cause an elevation in SDMA concentration.
How do I reorder Catalyst SDMA slides?
To reorder Catalyst SDMA slides, sign in to your IDEXX Online Orders account.
Don't have IDEXX Online Orders? Call your IDEXX representative: 24055110.
Two options: same reliable results
![]() The in-house Catalyst SDMA Test, with multiple SDMA-inclusive profiles to meet your patient and practice needs.
The in-house Catalyst SDMA Test, with multiple SDMA-inclusive profiles to meet your patient and practice needs.
![]() The IDEXX SDMA Test, included with every chemistry panel or as a stand-alone test from IDEXX Reference Laboratories.
The IDEXX SDMA Test, included with every chemistry panel or as a stand-alone test from IDEXX Reference Laboratories.
Note: SDMA is symmetric dimethylarginine.
For a complete list of references, visit idexx.com/sdma.
The information contained herein is intended to provide general guidance only. As with any diagnosis or treatment, you should use clinical discretion with each patient based on a complete evaluation of the patient, including history, physical presentation, and complete laboratory data. With respect to any drug therapy or monitoring program, you should refer to product inserts for a complete description of dosages, indications, interactions, and cautions. Diagnosis and treatment decisions are the ultimate responsibility of the primary care veterinarian